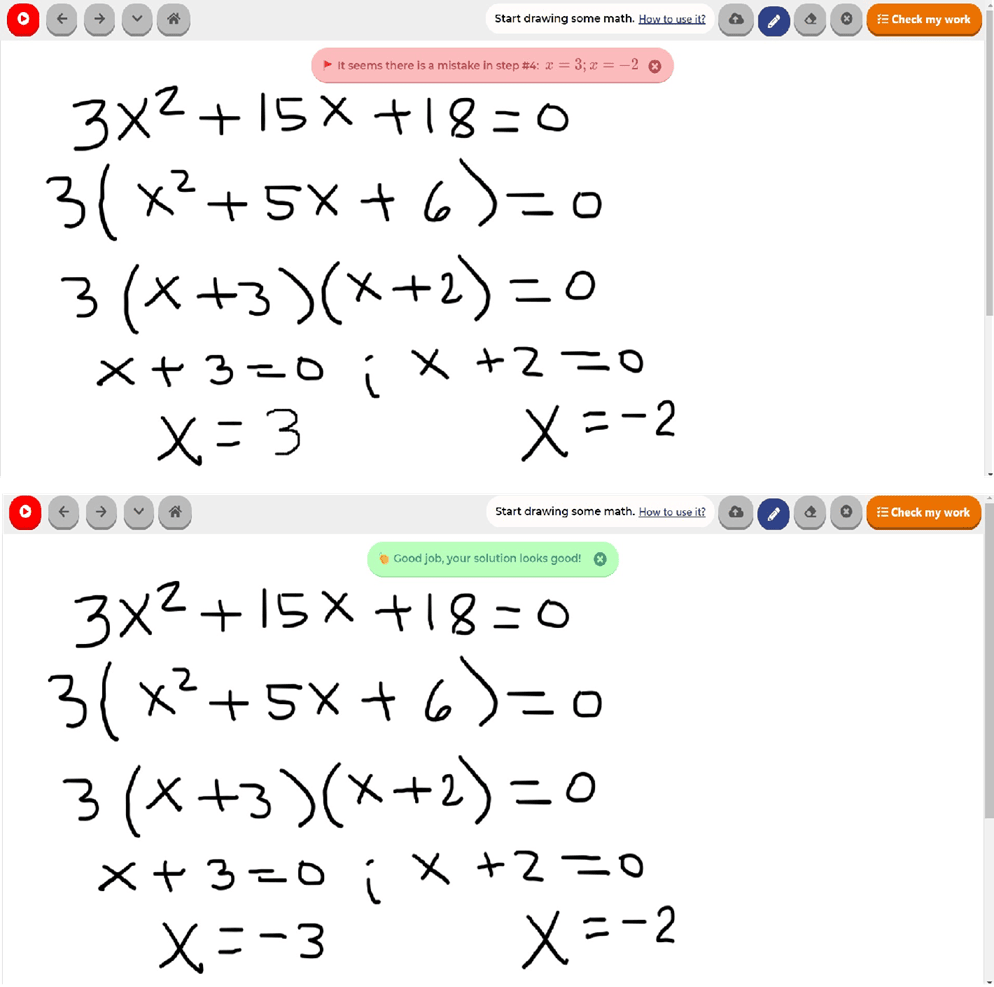
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
How should I solve this problem?
- Dimostrare da RHS (lato destro)
- Dimostrare dal LHS (lato sinistro)
- Esprimere tutto in seno e coseno
- Equazione differenziale esatta
- Equazione differenziale lineare
- Equazione differenziale separabile
- Equazione differenziale omogenea
- Prodotto di binomi con termine comune
- Metodo FOIL
- Load more...
Starting from the right-hand side (RHS) of the identity
Apply the trigonometric identity: $\sin\left(2\theta \right)$$=2\sin\left(\theta \right)\cos\left(\theta \right)$
Apply the formula: $\frac{a}{a}$$=1$, where $a=\sin\left(x\right)$ and $a/a=\frac{2\sin\left(x\right)\cos\left(x\right)}{\sin\left(x\right)}$
Combine all terms into a single fraction with $\cos\left(x\right)$ as common denominator
Apply the trigonometric identity: $\cos\left(2\theta \right)$$=2\cos\left(\theta \right)^2-1$
Apply the formula: $-\left(a+b\right)$$=-a-b$, where $a=2\cos\left(x\right)^2$, $b=-1$, $-1.0=-1$ and $a+b=2\cos\left(x\right)^2-1$
Cancel like terms $2\cos\left(x\right)^2$ and $-2\cos\left(x\right)^2$
Apply the trigonometric identity: $\frac{n}{\cos\left(\theta \right)}$$=n\sec\left(\theta \right)$, where $n=1$
Since we have reached the expression of our goal, we have proven the identity